Physiotherapy & Pain Management Clinic
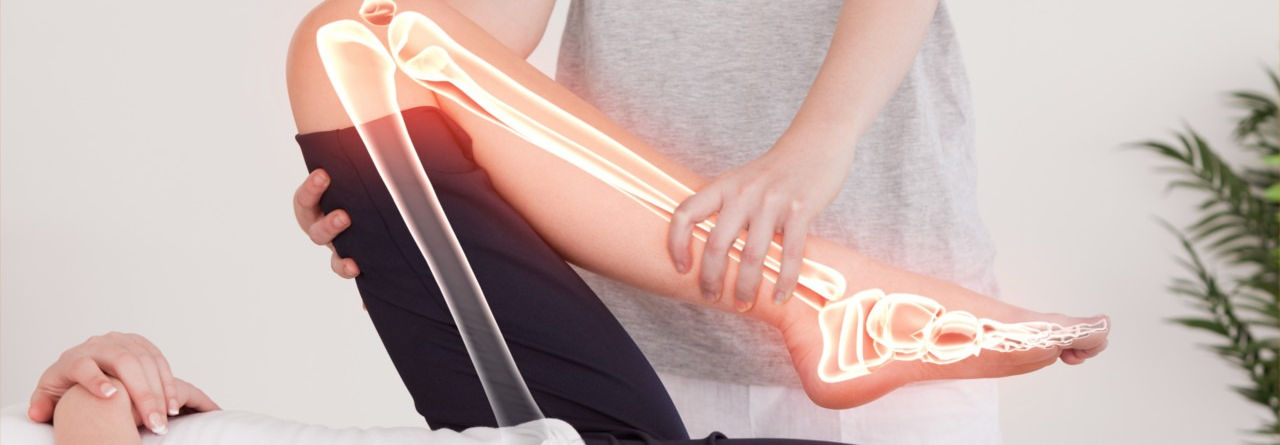
Physiotherapy
To restore, maintain, and maximize the physical strength, function, and overall well-being of adult and children

Heat Therapy
Applying heat can help improve your blood flow especially at the site of injury, thus, speeding up healing. In addition, it can help soften tight tissues and relieves pain.

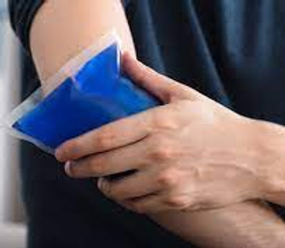
Cold Therapy
Cold therapy is effective in minimizing pain and swelling, especially in acute (immediate) injuries. It may also be used just after deep kneading massage (DKM). Examples of cold therapy are ice pack application and ice massage.
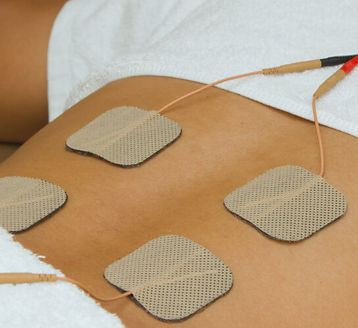
Electrical Stimulation
Electrical stimulation is used to prevent muscle atrophy (wasting) in people with paralysis and assist in gaining some degree of muscle strength, such as after a knee surgery. In electrical stimulation, electrodes are placed on the surface of the skin, which can cause muscles to shorten.

Range of Motion (ROM) Exercises
Range of motion exercises are often prescribed to increase or maintain flexibility of your joints and to reduce stiffness. There several types of range of motion exercises often prescribed including the following:
-
Passive Range of Motion (PROM) Exercises
-
Active Assistive Range of Motion(AAROM) Exercises
-
Active Range of Motion (AROM) Exercices
Strengthening Exercises
Certain conditions can make your muscles to become weak. Strengthening exercises is an important part of physiotherapy rehabilitation to prepare you for your return to your original performance level or highest possible function.
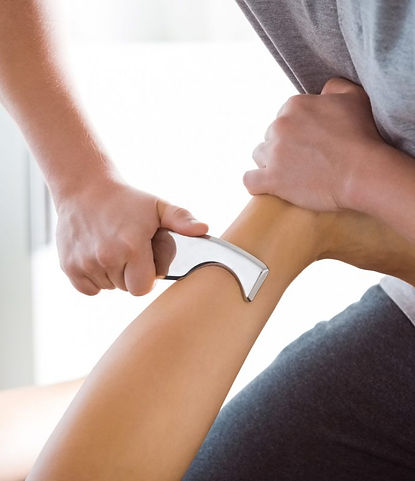
Soft Tissue Mobilization
Soft tissue mobilization or therapeutic massage may be a part of your physiotherapy treatment to relax your tight muscles, relieve pain and reduce swelling. Graston Technique , myofascial release , Gua sha. The following are other physiotherapy treatments.
-
Joint Mobilization
-
Gait (Walking)
-
Training / Assistive
-
Device Training
-
Postural Training
-
Ergonomic training
-
Balance Exercises
-
Traction
-
Taping
-
Bandaging
-
Fitting of Orthosis
-
Lymphatic drainage
Manual Therapy
Manual therapy (sometimes called bodywork) is a general term for treatment performed mostly with the hands. The goals of manual therapy include relaxation, decreased pain, and increased flexibility. Manual pressure technique can help relax muscles, increase circulation, and ease pain in the soft tissues.
-
Performing your daily tasks safely.
-
Protecting your joints and avoiding reinjury.
-
Using assistive devices such as crutches or wheelchairs.
-
Doing home exercises designed to help with your injury or condition.
-
Making your home safe for you if you have strength, balance, or vision problems.
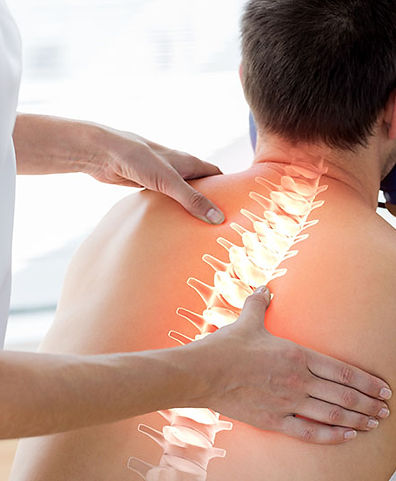
Types of Physiotherapy Treatments
& Interventions
The types of physiotherapy treatments vary and depends on your particular muscular or skeletal condition. Often, physiotherapy treatments are specifically made for one person and may not be the same for another with the same condition. Treatments are “tailor-made” for your particular problems and goals.
Special Treatments

Heat Therapy
To help relax and heal your muscles and soft tissues by increasing blood circulation.

Ultrasound Therapy
Which uses high-pitched sound waves to ease muscle spasms and relax and warm muscles before exercise


Cold & Ice
To relieve pain, swelling, and inflammation from injuries and other conditions such as arthritis.
.png)
Electrical Stimulation
This is the use of electrical current to create an effect in the body. It can also be used to cause muscles to contract.
Physical Therapy & Chronic Health Conditions
Physical therapy can help you live more easily with chronic or ongoing health conditions such as spinal stenosis, arthritis, and Parkinson’s disease. Your physical therapist will work with you to establish your goals. Then he or she will create a program of educational, range-of-motion, strengthening, and endurance activities to meet your needs.
Physical Therapy & Significant Health Conditions of Childhood
Physical therapists also work with children who have major injuries or health conditions, such as cerebral palsy. They address the usual issues of range of motion, strength, endurance, and mobility. Also, the therapist considers the child’s special growth and developmental needs
